Verb Tenses List
Verb Tenses are all used to express action that has taken place in the past, present, and future. The following sections will show how and when to use the 12 basic tenses in English grammar.

Present Simple Tense | Picture

Present Continuous Tense | Picture

Present Perfect Tense | Picture

Present Perfect Continuous Tense | Picture

Past Simple Tense | Picture

Past Perfect Tense | Picture

Past Perfect Continuous Tense | Image

Simple Future Tense | Picture

Future Continuous Tense | Picture

Future Perfect Tense | Picture

Future Perfect Continuous Tense | Picture

Verb Tenses Chart – All Tenses in a Table

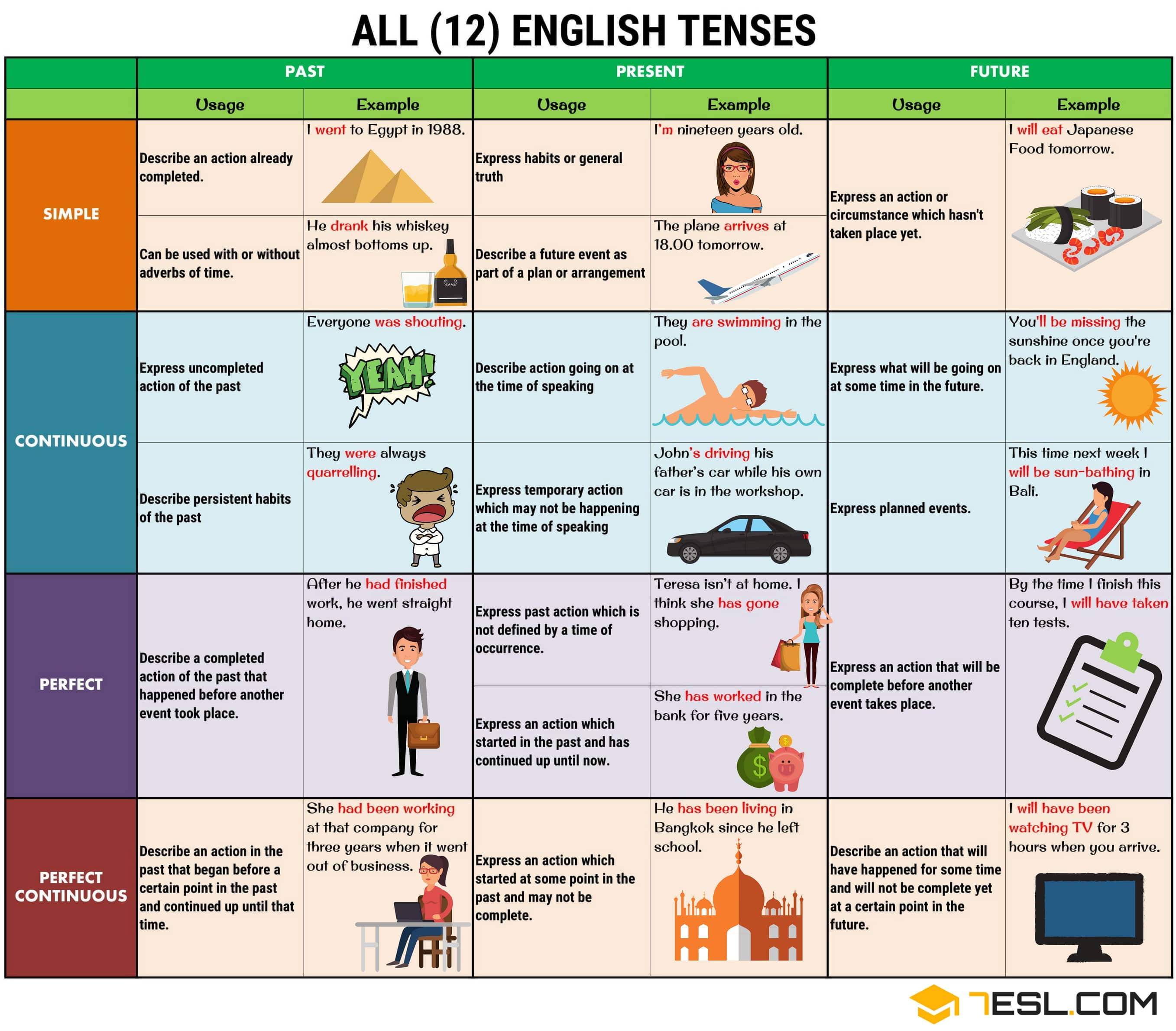
Comparison of Verb Tenses in English Grammar
Present Simple vs. Present Continuous
Learn the difference between Present Simple and Present Continuous tense with examples and useful grammar rules.
- The present simple tense is used to express general truths, while the present continuous tense describes actions happening now.
- The present simple tense is used to indicate present habits, while the present continuous tense is used to express annoying habits (+ always).
- The present simple tense expresses timetable events; the present continuous tense is used to describe future arrangements.
- The present simple tense is used to indicate permanent states; In contrast, the present continuous tense is used to express temporary states.
Present Simple vs. Present Continuous | Picture

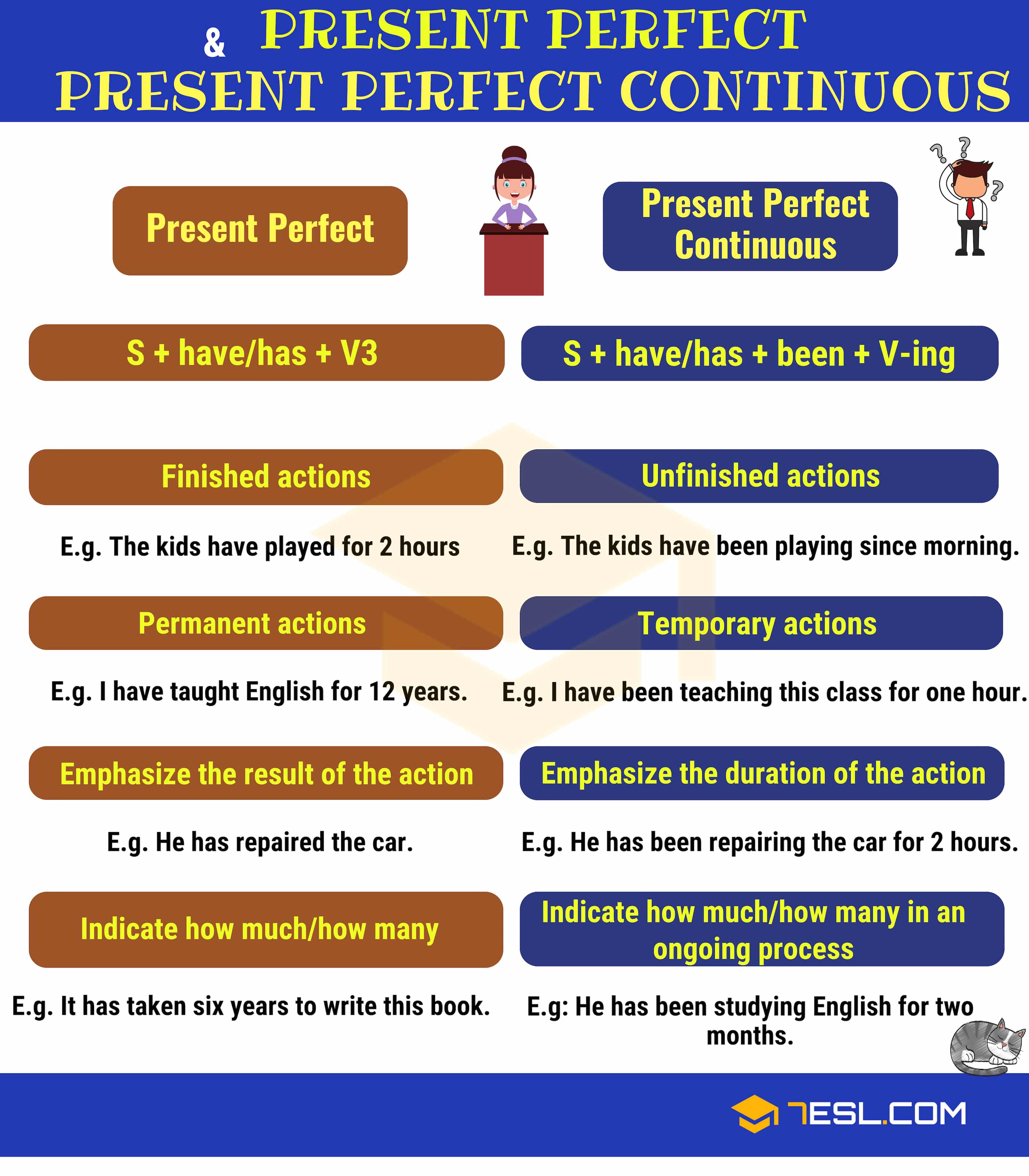
Present Perfect vs. Present Perfect Progressive
Learn the difference between the Present Perfect and Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English.
- The present perfect tense is used with finished actions, while the present perfect progressive tense is used with unfinished actions.
- The present perfect tense indicates permanent actions; the present perfect progressive tense describes temporary actions.
- The present perfect tense emphasizes the result of the action; In contrast, the present perfect progressive tense emphasizes the duration of the action.
- The present perfect tense indicates “How much/How many“, while the present perfect progressive tense indicates “How long something has been happening“.
Present Perfect vs. Present Perfect Progressive | Picture
Past Simple vs. Present Perfect
What is the difference between Past Simple and Present Perfect Tense?
- The past simple tense is used to express finished time; in contrast, the present perfect tense describes unfinished time.
- The past simple tense is used to refer to definite time, while the present perfect tense refers to indefinite time.
- The past simple tense indicates series of finished actions or repeated actions; the present perfect tense expresses experience or result.
Past Simple vs. Present Perfect | Picture

Past Perfect vs. Past Perfect Continuous
What is the difference between Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous Tense?
- The past perfect tense expresses a past action, already finished when another past action happened; the past perfect continuous tense describes a past action which started in the past and continued to happen after another action or time in the past.
- The past perfect tense emphasizes the result of an activity in the past; in contrast, the past perfect continuous tense emphasizes the duration of an activity in the past.
- The past perfect tense shows two events in the past that are linked, while the past perfect continuous tense shows the cause of a past action.
Past Perfect vs. Past Perfect Continuous | Picture

Will vs. Going to
Learn the Difference Between Will vs Going to in English with grammar rules and examples.
In English grammar, both “Will” and “Be Going to” are used to express future tense but they do not have the same meaning.
- Will is used to express future actions decided at the moment of speaking, while Going to describes future plans decided before the moment of speaking.
- Will is used to indicate a prediction based on personal opinions or experiences, while going to is used to express a prediction based on present evidence.
- Will expresses a future fact; going to is used to describe something is about to happen.
Will vs. Going to | Picture







0 comments:
Post a Comment